Menu
Vane pumps are used across automotive, industrial, aerospace, and commercial sectors where consistent fluid handling at moderate pressures is required. The automotive industry relies on them for power steering systems, automatic transmissions, and engine lubrication. Industrial applications include hydraulic machinery, chemical processing, and fuel transfer systems. These pumps also serve critical functions in aviation hydraulics, HVAC refrigeration, food processing, and pharmaceutical manufacturing due to their ability to deliver steady flow with minimal pulsation while handling low to medium viscosity fluids.
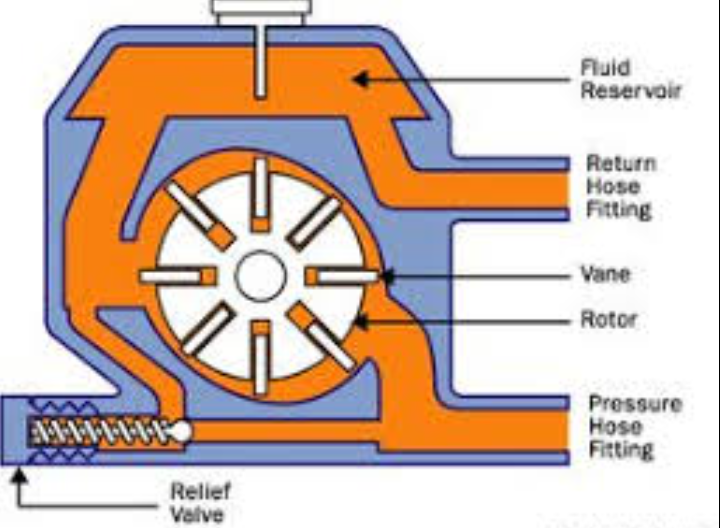
The automotive sector represents one of the largest markets for vane pumps, with applications spanning multiple vehicle systems. Power steering systems predominantly use balanced vane pumps that can deliver pressures between 1,400 and 1,500 psi. These pumps maintain contact with the cam ring through two inlets and outlets positioned 180 degrees apart, which balances the forces and reduces stress on the drive shaft. Variable displacement vane pumps have become increasingly popular in modern vehicles because they eliminate surplus flow at mid and high engine speeds, reducing energy consumption by up to 20% compared to fixed displacement designs.
Automatic transmissions employ vane pumps to circulate transmission fluid throughout the gearbox. This fluid serves dual purposes: it lubricates moving components to minimize friction and provides the hydraulic pressure needed for gear changes. The pumps must maintain a steady flow rate across varying engine speeds and loads, ensuring smooth gear transitions regardless of driving conditions. In vehicles with continuously variable transmissions, vane pumps work in tandem with electronic controls to adjust hydraulic pressure dynamically based on acceleration demands.
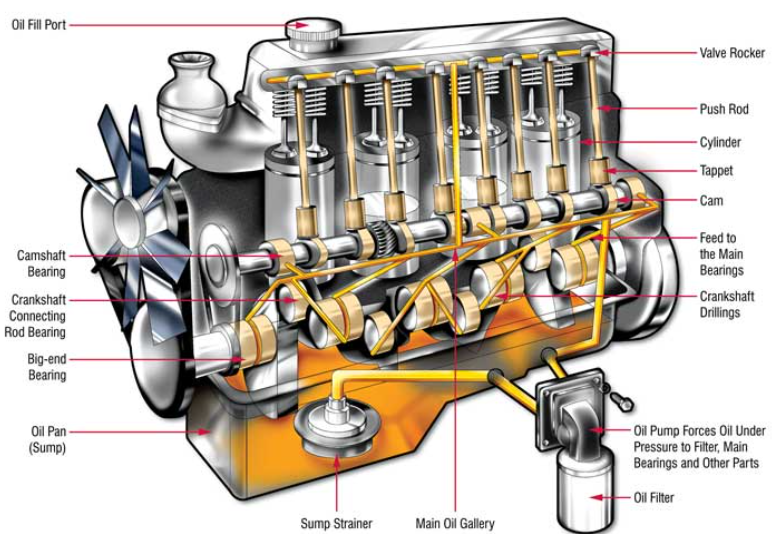
Engine lubrication systems also incorporate vane pumps, particularly in high-performance and diesel applications. These pumps circulate oil through the engine block, maintaining the protective film between moving parts that prevents metal-to-metal contact. The self-priming capability of vane pumps proves especially valuable during cold starts when oil viscosity is higher and rapid circulation is critical.
Manufacturing facilities and construction equipment depend heavily on hydraulic vane pumps for power transmission. These pumps convert mechanical energy from electric motors or combustion engines into hydraulic pressure that drives actuators, cylinders, and motors. The global hydraulic vane pump market reached $11.65 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a 4.5% compound annual growth rate through 2031, driven primarily by industrial automation and construction activity.
Mobile equipment like excavators, loaders, and cranes uses vane pumps in their hydraulic circuits. The compact design and high power-to-weight ratio make them ideal for space-constrained installations on mobile machinery. Heavy-duty vane pumps account for approximately 32% of the market by product type, reflecting their prominence in demanding industrial applications where reliability under continuous operation is essential.
Plastic injection molding machines utilize vane pumps to generate the hydraulic force needed for clamping molds and injecting material. The consistent flow characteristics ensure uniform pressure distribution, which directly affects part quality and production cycle times. Similarly, hydraulic presses employ vane pumps to deliver the substantial forces required for metal forming, stamping, and assembly operations.
Aircraft hydraulic systems represent a critical application where vane pumps must meet stringent reliability and performance standards. These pumps power landing gear actuation, flight control surfaces, and braking systems. Aviation accounts for roughly 24% of the vane pump market by end-use industry, reflecting the technology’s importance in aircraft operations.
The aviation industry favors vane pumps for several reasons. First, they provide consistent output pressure necessary for precise control surface positioning. Second, their relatively quiet operation compared to gear pumps reduces cabin noise in pressurized aircraft. Third, they handle aviation hydraulic fluids across wide temperature ranges encountered during flight, from subzero temperatures at altitude to elevated temperatures near engine compartments.
Larger aircraft require more extensive hydraulic systems, which translates to greater vane pump capacity. Commercial jetliners typically employ multiple redundant hydraulic circuits, each powered by dedicated vane pumps. This redundancy ensures that critical flight controls remain operational even if one hydraulic system fails. Fuel transfer systems in both commercial and military aircraft also use vane pumps to move fuel between tanks, maintaining proper weight distribution throughout the flight envelope.
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems use vane pumps to circulate refrigerants through evaporator and condenser coils. The pumps handle refrigerants including ammonia, various freon compounds, and newer environmentally friendly alternatives. Their ability to maintain steady flow rates while operating quietly makes them well-suited for commercial and residential climate control applications.
Air conditioning installation and servicing relies on rotary vane vacuum pumps to evacuate refrigerant lines before charging systems. This process removes air and moisture that could otherwise compromise system efficiency or cause corrosion. The pumps must achieve vacuum levels sufficient to boil off residual moisture, typically below 500 microns of pressure.
Industrial refrigeration systems in food processing and cold storage facilities employ larger vane pumps capable of handling high refrigerant volumes. These installations often run continuously, making the durability and low maintenance requirements of vane pumps particularly valuable. The pumps’ volumetric efficiency remains relatively constant across varying suction and discharge pressures, which helps maintain consistent cooling performance.
Food processing operations use vane pumps for transferring liquids with varying viscosities, including oils, syrups, sauces, and concentrates. The gentle pumping action minimizes shear forces that could damage delicate products or alter their texture. Flexible vane pumps, which use elastomeric rotors, are especially popular in food applications because they provide sanitary operation and easy cleaning.
Fountain drink dispensers and commercial espresso machines rely on small vane pumps to deliver precise fluid volumes. In carbonated beverage systems, the pumps transport water into pressurized CO2 tanks for carbonation, then deliver the finished product to dispensing valves. The steady flow characteristic ensures consistent carbonation levels and portion sizes.
Vacuum packaging systems in the food industry use rotary vane vacuum pumps to remove air from packaging before sealing. This extends shelf life by limiting oxidation and bacterial growth. The pumps must handle moisture-laden air drawn from fresh products without suffering corrosion or performance degradation. Freeze-drying operations also depend on vane vacuum pumps to maintain the low pressures necessary for sublimation of ice directly to vapor, preserving the structure and nutrients of foods like fruits and vegetables.
Pharmaceutical manufacturing demands pumps that can handle both aggressive chemicals and maintain contamination-free operation. Rotary vane vacuum pumps are used in tablet coating processes, where controlled vacuum conditions ensure even application of protective and functional coatings. They also facilitate vacuum filling of vials and ampules, preventing air bubble entrapment that could affect dosing accuracy.
Freeze-drying of pharmaceuticals represents a major application where maintaining precise vacuum levels is critical for product stability. The pumps remove water vapor during the sublimation phase while keeping chamber pressure low enough to prevent the product temperature from rising above its critical threshold. This process preserves the chemical structure of heat-sensitive medications and biological compounds.
Laboratory equipment including vacuum ovens, rotary evaporators, and mass spectrometers incorporates vane vacuum pumps. These instruments require stable vacuum conditions for reliable analytical results. The pumps’ ability to maintain consistent vacuum levels over extended periods makes them suitable for long-duration experiments and continuous analytical workflows.
Chemical plants use vane pumps to transfer low-viscosity solvents, acids, and process fluids. The pumps can be constructed with corrosion-resistant materials including stainless steel and specialized alloys to handle aggressive chemicals safely. Their sealed design prevents leaks that could pose environmental or safety hazards.
Distillation and vacuum drying operations in chemical manufacturing employ rotary vane vacuum pumps to create the reduced-pressure environments needed for separating components with close boiling points or processing temperature-sensitive materials. Oil-lubricated rotary vane pumps excel at removing water vapor from solvents and degassing liquids, though dry-running variants are preferred when oil contamination must be avoided.
Solvent recovery systems use vane pumps to maintain the vacuum needed for condensing and capturing volatile organic compounds. This reduces emissions while recovering valuable materials for reuse. The pumps handle vapor-laden airstreams that would quickly degrade other pump types, making them economical choices for continuous solvent recovery operations.
Fuel loading terminals and transport vehicles use vane pumps to transfer gasoline, diesel, aviation fuel, and liquefied petroleum gas. These pumps handle the low-viscosity petroleum products efficiently while providing the flow rates necessary for rapid tank filling. Their self-priming capability allows them to draw fuel from below-grade storage tanks without external priming systems.
LPG and ammonia transfer applications benefit from vane pumps’ ability to handle liquefied gases under pressure. The pumps maintain seal integrity while dealing with fluids that can vaporize if pressure drops occur. Bulk transportation trucks and rail cars incorporate vane pumps in their loading and unloading systems.
Offshore drilling operations use hydraulic vane pumps in blowout preventers and other safety-critical systems. The pumps must deliver reliable performance in harsh marine environments with salt spray, temperature extremes, and constant vibration. Redundant pump systems ensure that well control equipment remains operational under all conditions.
The semiconductor industry requires ultra-high vacuum conditions for wafer processing, thin-film deposition, and lithography. While achieving the ultimate vacuum levels requires specialized pumps, rotary vane vacuum pumps serve as roughing pumps that reduce pressure from atmospheric levels to the range where high-vacuum pumps can take over efficiently.
Semiconductor fabrication facilities use dry-running rotary vane pumps to avoid oil contamination that would ruin sensitive wafer surfaces. These pumps evacuate process chambers between production steps and maintain vacuum in load-lock chambers used to transfer wafers without breaking the main chamber vacuum. The CHIPS and Science Act investments in semiconductor manufacturing are driving increased demand for vacuum equipment including vane pumps.
Chemical vapor deposition systems employ vane pumps to control chamber pressure during film growth. The pumps must handle corrosive process gases and byproducts without degrading. Regular maintenance ensures they continue meeting the strict cleanliness standards required in semiconductor production.
Excavators, bulldozers, and other heavy equipment use vane pumps in their hydraulic systems to power boom cylinders, bucket actuators, and track drives. The pumps convert engine power into hydraulic pressure that can exert tremendous force for earth-moving operations. Variable displacement vane pumps in these applications adjust output to match hydraulic demand, improving fuel efficiency compared to fixed displacement designs.
Mining equipment faces particularly severe duty cycles with high loads, contaminated hydraulic fluid, and harsh environmental conditions. Vane pumps selected for mining applications feature hardened vanes, robust housings, and effective filtration to extend service life despite these challenges. Regular oil analysis and filtration system maintenance help prevent premature wear from abrasive particles that inevitably enter hydraulic circuits.
Agricultural machinery including tractors and combine harvesters relies on vane pumps for implement hydraulics and steering assistance. The pumps must operate reliably across wide temperature ranges from winter fieldwork to summer harvests. Their ability to self-prime proves valuable when restarting equipment after maintenance or off-season storage.
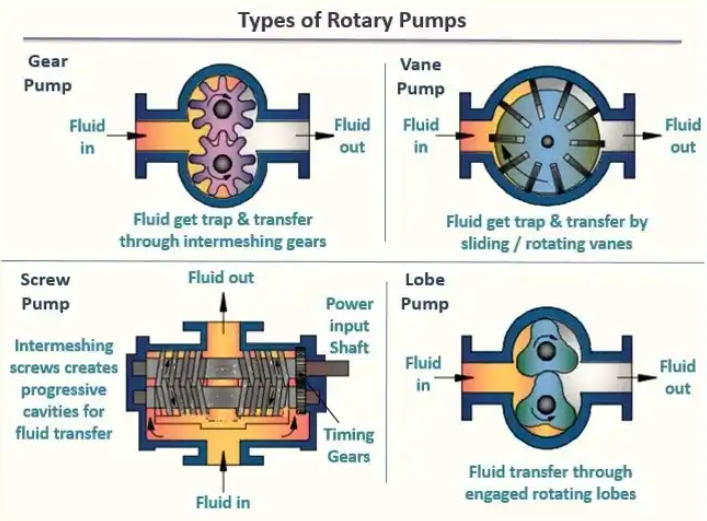
Vane pumps work best with low to medium viscosity fluids, typically from thin liquids like solvents and gasoline up to moderate-viscosity oils. They struggle with highly viscous fluids above 300-400 centistokes because thick fluids prevent the vanes from sliding freely in their slots. For high-viscosity applications, heating jackets can be added to reduce fluid viscosity and improve pumpability.
Vane pumps deliver the constant flow and quick pressure response needed for responsive steering feel. Their balanced design with dual inlets and outlets eliminates the side loads that would stress bearings in unbalanced configurations. They also operate quietly compared to gear pumps, improving driver comfort. Modern variable displacement vane pumps further reduce energy consumption by adjusting output to match steering demand.
Vane pumps can tolerate small amounts of suspended solids, but abrasive particles accelerate vane wear and reduce pump life. Effective filtration is essential to protect the pump from debris. Applications with significant solid content are better served by other pump types like progressive cavity or air-operated diaphragm pumps that tolerate particulates more readily.
Regular maintenance includes checking and replacing the vanes as they wear, monitoring lubricant quality and level in oil-lubricated designs, inspecting seals for leaks, and ensuring inlet filters remain clean. Vanes are inexpensive wear items designed for easy replacement. Most industrial vane pumps can operate thousands of hours between major services when properly maintained with clean fluid and appropriate filtration.
North America dominates the vane pump market with over 40% of global revenue, driven by established automotive, aerospace, and industrial sectors. The United States alone accounts for significant market share due to ongoing manufacturing activity and infrastructure development. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region with an expected compound annual growth rate exceeding 11% through 2032, fueled by rapid industrialization in China, India, and Southeast Asian nations.
India’s expanding automotive industry particularly drives vane pump demand, with car ownership projected to increase from 22 vehicles per 1,000 people currently to 150 per 1,000 by 2040—a 775% growth that will require millions of additional vane pumps for power steering and transmission systems. China’s manufacturing sector expansion and infrastructure investments create substantial demand for hydraulic vane pumps in construction equipment and industrial machinery.
Europe maintains a strong vane pump market supported by advanced manufacturing, stringent environmental regulations driving efficient hydraulic systems, and a large installed base of industrial equipment. The region’s focus on energy efficiency and sustainability encourages adoption of variable displacement and energy-optimized vane pump designs that reduce operational costs and carbon emissions.
The market dynamics reflect broader trends toward industrial automation, electrification of transportation, and increasing precision in manufacturing processes. As factories implement Industry 4.0 technologies, demand grows for pumps with digital connectivity and remote monitoring capabilities, pushing vane pump manufacturers to integrate sensors and communication interfaces into their products.
Vane pumps fill a valuable niche in fluid handling where their combination of steady flow, compact size, quiet operation, and moderate pressure capability aligns with application requirements. Understanding which industries and systems rely on them helps explain both their widespread adoption and the specific engineering choices that make them well-suited for each application. Their continued evolution through variable displacement designs, advanced materials, and digital integration ensures they’ll remain relevant across industrial sectors for years to come.