Menu
What is commonly called multi-way valve in China belongs to the sectional type, primarily meeting the needs of mobile hydraulics: only one pump, but multiple hydraulic cylinders need to be driven separately. Generally, one control section controls one (group) of hydraulic cylinders, with multiple control sections sharing supply and return oil, with connection ports arranged on the oil source section; the oil source section is often arranged on one side, so it is also called the head section, and there is also an end section used to block oil ports. The inlet and return ports of each section are positioned the same and can be bolted together. When there are many control sections, to reduce flow passage pressure loss, the oil source section can be arranged in the middle (requiring two end sections), or two oil source sections can be installed (no end sections needed). Valve bodies mostly use casting to facilitate the formation of curved flow passages and reduce pressure loss; to ensure pressure resistance and durability, high-grade ductile iron or vermicular graphite iron is mostly used. Some manufacturers also use rolled steel blocks (resistant to high pressure, but flow passages need to be formed by drilling, resulting in greater pressure loss).

When sectional valves were first invented, they only had directional control functions. Later, throttling grooves were opened on the valve spool, becoming directional throttle valves (capable of simultaneously controlling the direction and speed of hydraulic cylinder movement). To protect the pump, a primary relief valve was added to the oil source section; to avoid overload damage to the hydraulic cylinders, a secondary relief valve was added to the control sections.
Subsequently, to prevent negative pressure from occurring in both chambers of the hydraulic cylinders, make-up valves were added; to reduce flow competition and load interference when multiple hydraulic cylinders move simultaneously, pre-positioned constant pressure differential elements (pressure compensating valves) were added, namely load-sensing valves; to meet the needs of equipment such as excavators, the LUDV form with post-positioned constant pressure differential elements emerged (still able to ensure uniform flow to each cylinder when pump flow is saturated).
All control elements are basically concentrated on the control sections, with a quite compact structure. Operating methods have gradually evolved from manual to hydraulic control, electro-proportional control, bus control, etc., with electronic control generally having auxiliary emergency manual operation.
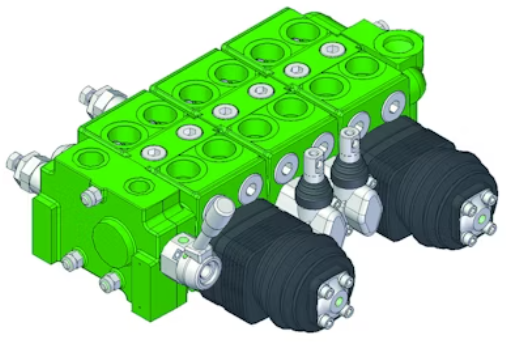
Sectional valves are widely used in mobile hydraulic equipment. Considering operating habits, this installation method will exist for quite a long time. Disadvantages of sectional valves: piping needs to be disassembled when replacing valve sections, which is troublesome and contaminants can easily enter; leakage between sections is prone to occur. The advantage of sectional valves is flexibility (install control sections as needed), but for large-volume standardized machinery with a fixed number of hydraulic cylinders (such as loaders and forklifts), this advantage is not prominent; if only two or three sections are needed, they are often made as one piece.
For large-volume host machines, some manufacturers replace multi-section combinations with integrated valve blocks, reducing leakage points and reducing external dimensions, but three difficulties need to be overcome: